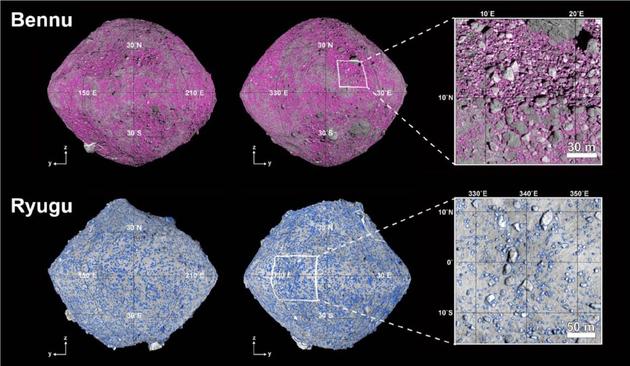
Using artificial intelligence technology, a University of Tokyo team has managed to rapidly identify from photographs the size, location and shape of some 200,000 rocks on two asteroids. https://www.japantimes.co.jp/news/2025/04/08/japan/science-health/japan-ai-technology-asteroid-rocks/?utm_medium=Social&utm_source=mastodon #japan #sciencehealth #ai #space #asteroids #hayabusa #ryugu #universityoftokyo