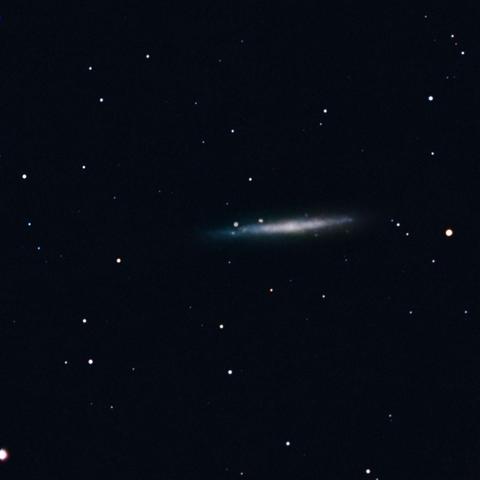
NGC4244.
ZWO Seestar S50.
250mm, f5, 465 exposures of 10’’.
#telescope #telescopes #zwo #zwoasi #zwoseestar #zwoseestars50 #seestar #seestars50 #astro #astrophoto #astrophotos #astrophotography #astrophotographer #spacephotography #astronomy #spaceexploration #nasa #universe #space #deepsky #deepsky #deepspace #galaxy #galaxies #ngc #ngc4244
Recent searches
Search options
#universe
Free download codes:
Michael HERTER - LAST
"Epic Cinematic Orchestral Trailer Soundtrack"
M81 - Bode's Galaxy.
ZWO Seestar S50.
250mm, f5, 427 exposures of 10’’.
#telescope #telescopes #zwo #zwoasi #zwoseestar #zwoseestars50 #seestar #seestars50 #astro #astrophoto #astrophotos #astrophotography #astrophotographer #spacephotography #astronomy #spaceexploration #nasa #universe #space #deepsky #deepsky #deepspace #galaxy #galaxies #bode #bodegalaxy #m81 #messier81 #messier #ngc3031
Today’s Image of the Day from the European Space Agency features the galaxy I Zwicky 18, which was captured in remarkable detail by the James Webb Space Telescope...
#imageoftheday #EuropeanSpaceAgency #dwarfgalaxy #jameswebbspacetelescope #photography #universe #space
https://www.earth.com/image/dwarf-galaxy-i-zwicky-18-has-a-youthful-appearance/
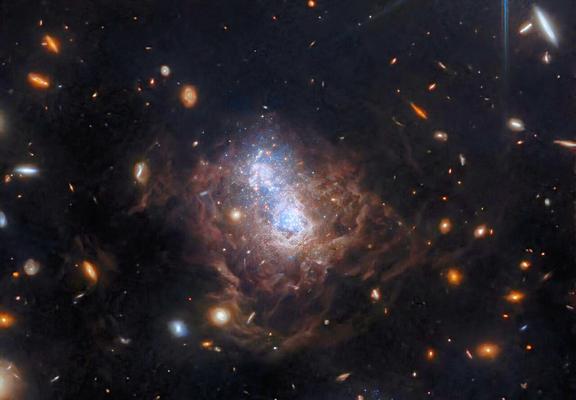

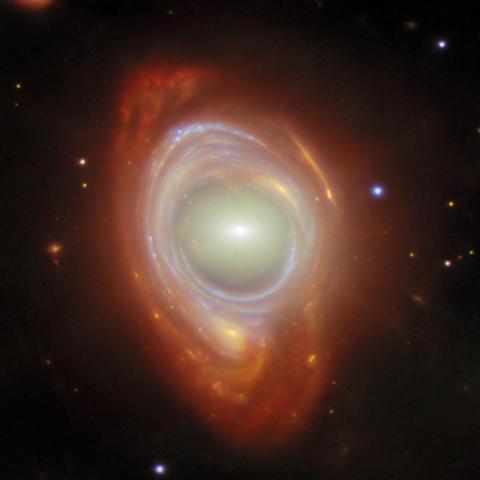
A rare cosmic phenomenon called an #Einstein ring.
There are two galaxies, separated by a large distance. The foreground galaxy is at the center, while the background galaxy appears to be wrapped around the closer galaxy, forming a ring.
The light from the more distant object is bent about a massive intermediate object because #spacetime, the fabric of the #Universe itself, is bent by mass, and therefore light travelling through #space and #time is bent as well.
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2025/03/Webb_spies_a_spiral_through_a_cosmic_lens
hello people!!1
new drums and bass!!
*
https://daroharutokei.bandcamp.com/track/dhk-el-destino-del-universo-2025
*
#dnb #drums #electronic #electronicmusic #indie #dance #music #musik #musica #dnbnation #tech #techno #technik #technology #nowplaying #now #nowlistening #song #play #universe #destiny #ListeningClub #listen #breaking #dhk #bass #bandcamp #BandcampFriday #cancion #thursday #track #synth #synthetizer #argentina #arg #culture #cultura
Universe’s First Light Has Just Been Revealed in Stunning Detail : ScienceAlert…
After five years of staring unblinking at the sky, the Atacama Cosmology Telescope #ACT has compiled the most detailed map we've ever seen of the cosmic microwave background – the faint light that permeates the #Universe from just 380,000 years after the #BigBang...

Wow, a stunning image by JWST of an Einstein ring, a more distant galaxy's light being bent by gravitational lensing around a much closer galaxy. The closer galaxy is an elliptical and the much more distant galaxy, which in this case is perfectly aligned behind the foreground elliptical thereby forming the ring, is a spiral galaxy. I think this beautiful image is going to be my desktop for awhile. Just stunning!
https://www.esa.int/ESA_Multimedia/Images/2025/03/Webb_spies_a_spiral_through_a_cosmic_lens

M42 Orion Nebula.
Celestron NexStar Evolution 6 + ZWO ASI585MC Pro.
300mm, f2, 400 exposures of 10’’.
#telescope #telescopes #celestron #celestrontelescope #celestronnexstar #nexstarevolution #nexstarevolution6 #zwo #zwoasi #zwoasi585mc #astro #astrophoto #astrophotos #astrophotography #astrophotographer #spacephotography #astronomy #spaceexploration #nasa #universe #space #deepsky #deepspace #nebula #orion #orionnebula #m42 #messier42 #messier
A "potentially hazardous" pyramid-size asteroid is about to zoom past Earth at around 48,000 mph (77,300 km/h) this week as it reaches its closest point to our planet in more than 100 years. But the hefty space rock poses zero risk of hitting us now or in the future, data shows. @LiveScience
https://www.livescience.com/space/asteroids/potentially-hazardous-pyramid-size-asteroid-will-make-its-closest-flyby-of-earth-for-more-than-100-years-this-wednesday
Back in 1915, Einstein put forth his most ambitious idea: the general theory of relativity, combining #gravity with #relativity to create an entirely new conception of our #Universe.
In most conventional circumstances, the predictions of Einstein’s theory are indistinguishable from that of its predecessor: Newton’s law of universal gravitation.
Is it possible, then, to somehow reduce Einstein’s equations down to Newton’s equations?
#physics
https://bigthink.com/starts-with-a-bang/turn-einsteins-equations-newtons-law/
Dark #energy is probably doing something weird, and we don’t know why.
Astronomers just announced they’re seeing more evidence that dark energy — the mysterious substance that pervades the #cosmos and causes the expansion of the #universe to accelerate — is not a constant over time, but may instead be weakening.
It means dark energy has changed over time, getting weaker and changes how we think the universe behaves in a fundamental way.
https://badastronomy.beehiiv.com/p/is-the-universe-misbehaving-again
The Brighter Side of News: Scientists think they discovered what existed before the Big Bang…
#Darkmatter has baffled physicists for nearly a century, quietly shaping our #universe 's unseen framework. Invisible yet influential, it provides the gravity necessary to hold #galaxies together... #science #space #physics #bigbang
Celestron NexStar Evolution 6 + ZWO ASI585MC Pro.
300mm, f2, 150 exposures of 30’’.
#telescope #telescopes #celestron #celestrontelescope #celestronnexstar #nexstarevolution #nexstarevolution6 #zwo #zwoasi #zwoasi585mc #astro #astrophoto #astrophotos #astrophotography #astrophotographer #spacephotography #astronomy #spaceexploration #nasa #universe #space #deepsky #deepspace #pleiades #maia #nebula #cluster #m45 #messier45 #messier
Most of the galaxies in the universe rotate in the same direction. Why this happens highlights a gap in our understanding of how the universe works. "It is still not clear what causes this to happen, but there are two primary possible explanations," says astronomer Lior Shamir of Kansas State University. @ScienceAlert explores both:
Who doesn’t love a good baby picture? The clearest and most precise images yet of the universe in its infancy — the earliest cosmic time accessible to humans — have been produced by an international team of astronomers. Phys.org has the story:
Webb reveals unexpected complex chemistry in primordial galaxy
(... what we think of as the "first billion years" of the universe probably took a more billion years than that)
https://phys.org/news/2025-03-webb-reveals-unexpected-complex-chemistry.html
The Rosette Nebula
The Rosette Nebula spans a distance of about 100 lightyears across and is located 5,000 lightyears from Earth in the Monoceros constellation. It's located near the Orion comstellation.
Free download codes:
Michael HERTER - AMBIENT
"subtle melodies and atmospheric soundscapes"
Oxygen discovered in most distant known galaxy
https://www.eso.org/public/news/eso2507/
#ycombinator #ESO #eso_org #Astronomy #Astrophysics #Astronomie #Suedsternwarte #telescopes #detectors #comets #planets #stars #galaxies #nebulae #universe #NTT #VLT #VLTI #ALMA #ELT #La_Silla #Paranal #Garching #Chile









 Hacker News
Hacker News